LangChain框架是一个非常强大的工具,它大大加快了LLM在项目和代理开发中的有效使用。该框架提供了一种高级抽象,允许开发人员立即开始使用模型并将其集成到他们的产品中。但是另一方面,了解LangChain的核心概念(例如Runnable的架构)对于构建LLM代理和链的开发人员非常有益,因为它提供了一种结构化的方法和对使用框架的洞察力。

LangChain架构基础
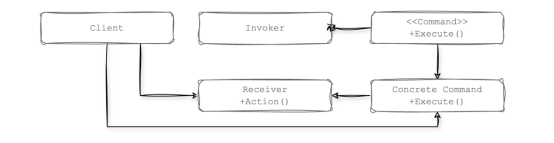
LangChain中的Runnable架构基于命令模式的原理构建,命令模式是一种将请求封装为对象的行为设计模式。这种设计有助于参数化、排队和动态执行命令,使Runnable对象在各种工作流中模块化、可组合和可管理。
Runnable对象特别适合工作流管理、顺序任务执行、处理条件逻辑以及与外部系统交互,它们提供灵活性、可重用性和模块化。你可以动态地将任务链接在一起以创建复杂的行为场景,同时保持干净且易于管理的代码结构。
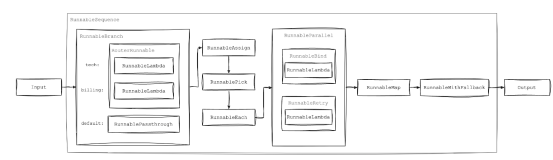 Runnable链的可能配置之一
Runnable链的可能配置之一
LangChain中执行特定任务的大多数高级对象都实现了Runnable类。你计划包含在链中的任何对象也必须以某种方式实现Runnable类。有趣的是,Runnable充当命令的抽象或一个具体命令,同时也充当了一个调用者和接收者角色。
一个值得注意的例子是此类中提供的管道方法,它专门用于创建链。此方法允许无缝组合多个Runnable,使其成为在LangChain中构建和执行工作流的基石。
在上图中,你可以看到Runnable如何与其各种实现一起运行。接下来,我们将在本文中详细研究这些实现。
创建Runnable
实际上,有两种方法可以创建Runnable:通过RunnableLambda或扩展基Runnable类。
将RunnableLambda用于简单函数
创建Runnable的最简单方法是使用RunnableLambda。此类允许你将任何函数包装为Runnable,从而允许动态行为而无需自定义类。
扩展Runnable基类
对于更高级的使用场景,你可以扩展Runnable基类。此方法可完全控制执行生命周期,包括调用、批处理和流等方法。
使用Runnable构建工作流
LangChain中的Runnable架构通过按功能分组的专用Runnable进行了扩展,使其用途广泛且适用于各种应用程序。
路由和分支类型
根据条件或输入管理执行流程的Runnable有:
RouterRunnable
根据给定的键值将输入定向到特定的Runnable,类似于switch-case语句。适用于基于运行时参数的动态任务执行。
RunnableBranch
根据条件检查从多个选项中执行特定的Runnable,使工作流能够适应不同的输入场景。
数据操作和分配类型
转换或准备数据以用于后续任务的Runnable有:
RunnableAssign
通过添加新字段或更新现有字段来增强或修改输入数据,为后续处理步骤做好准备。
RunnablePick
从输入数据中选择并提取特定字段,从而可以对相关信息进行重点处理。
RunnablePassthrough
不做任何更改地传递输入数据,这对于维护工作流中的数据完整性非常有用。
RunnableMap
将转换应用于映射对象中的每个字段,从而实现对键值对的单独处理。
序列和工作流组合类型
可按顺序构造和执行任务的Runnable,支持创建复杂的工作流:
RunnableSequence
以线性方式链接多个Runnable,其中一个Runnable的输出成为下一个Runnable的输入,形成逐步处理的管道结构。
RunnableEach
将Runnable应用于集合中的每个元素,类似于数组上的映射函数,允许批处理。
RunnableParallel
在同一输入上同时执行多个Runnable,从而实现并发处理以提高效率。
错误处理、弹性和配置类型
通过重试机制和回退选项增强稳健性的Runnable有:
RunnableBinding
通过预设某些参数或配置创建自定义Runnable,允许针对特定上下文定制可重复使用的组件。
RunnableRetry
根据指定的重试策略在失败时自动重试Runnable,增强对瞬态错误的恢复能力。
RunnableWithFallbacks
如果主Runnable失败,则提供要执行的替代Runnable,以确保工作流程可以继续或正常降级。
整合
在前面的部分中,我们探讨了单个Runnable及其在构建模块化工作流中的作用。现在,让我们看看如何组合这些Runnable来创建全面的实际应用程序。以下三个示例演示了如何集成多个Runnable来解决复杂问题。
示例1:智能文档处理管道
现在,我们假定有一家公司希望自动处理发票、收据和合同等传入文档。开发的软件系统目标是对文档类型进行分类、提取相关数据、验证数据并将其存储在数据库中,并且能够妥善处理错误,并在发生瞬时故障时重试操作。
使用的Runnable有RunnableSequence、RouterRunnable、RunnableParallel、RunnableRetry、RunnableWithFallbacks、RunnableAssign、RunnableLambda等,关键代码如下:
在上面代码中,工作流首先使用ocrRunnable将文档图像转换为文本。提取的文本被分类为文档类型(发票、合同或收据)。RouterRunnable根据文档类型将文本定向到适当的数据提取Runnable。提取的数据经过验证,然后保存到数据库。RunnableRetry确保在发生瞬时故障时重试保存最多三次。如果任一步骤失败,RunnableWithFallbacks会提供回退消息以妥善处理错误。
示例2:个性化推荐引擎
电子商务平台希望根据用户的浏览历史和偏好为他们提供个性化的产品推荐。
使用的Runnable有RunnableParallel、RunnableMap、RunnableBranch、RunnableWithFallbacks等,相关代码如下:
在上面代码中,工作流首先使用RunnableParallel同时获取用户的浏览历史、购买历史和个人资料。然后,使用RunnableMap单独处理每条数据,为生成推荐做好准备。
RunnableBranch根据用户的个人资料决定使用哪种推荐算法:
- 如果用户是高级会员(isPremiumMembe为true),则使用premiumUserRecommendations。
- 如果用户没有购买历史(表示是新用户),则使用newUserRecommendations。
- 否则,默认为regularUserRecommendations。
如果推荐过程中的任一步骤失败,RunnableWithFallbacks可确保系统提供一组默认推荐,从而保持良好的用户体验。
最后,RunnableSequence协调整个工作流,确保每个步骤都按正确的顺序进行。工作流通过使用userId调用来执行,并根据用户的数据输出个性化推荐。
示例3:用于分析的数据处理管道
现在,我们假定有一家公司需要处理大型数据集以生成涉及数据清理、转换、分析和可视化的分析报告。
使用的Runnable有RunnableSequence、RunnableEach、RunnableRetry、RunnableBinding,关键代码如下:
上述代码中,此工作流处理来自不同来源的多个数据集的数据处理。首先,定义一个使用RunnableBinding绑定到特定数据源的fetchData可运行程序。每个数据获取操作都使用RunnableRetry包装,通过重试最多三次来处理瞬时故障。
从每个源获取的数据经过RunnableSequence定义的一系列处理步骤:
- 数据清理:删除或更正错误数据。
- 数据转换:将数据转换为适合分析的格式。
- 数据分析:执行分析计算。
- 数据可视化:生成针对分析结果的可视化表示。
在此,使用RunnableEach来并行处理多个数据集。这个对象将相同的处理顺序应用于每个数据集上。
结论
总体来看,LangChain中的Runnable架构是构建涉及大型语言模型(LLM)的复杂模块化工作流的强大基础。在本文中,我们探讨了如何创建和组合各种Runnable以应对各种挑战:
- 路由和分支:利用RouterRunnable和RunnableBranch可以根据运行时条件实现动态执行路径。
- 数据操作和分配:RunnableAssign、RunnablePick和RunnableMap等工具提供灵活的数据转换功能,为后续处理步骤准备输入。
- 序列和工作流组合:通过使用RunnableSequence、RunnableEach和RunnableParallel链接任务,开发人员可以协调流程,无论它们是需要顺序执行还是并行处理。
- 错误处理和弹性:借助RunnableRetry和RunnableWithFallbacks,工作流可以优雅地处理错误并提供回退机制。
总之,Runnable提倡了一种结构化的方法来构建LLM代理和链。最后,在你计划将LangChain集成到实际项目中时,请认真考虑Runnables如何增强你的工作流,使其更灵活、更有弹性且更易于维护。
文章来自:51CTO
