引言:RAG技术为何成为企业AI应用首选
实现成本降低千倍、响应速度秒级的企业级知识库解决方案
在当前AI技术飞速发展的背景下,企业面临着一个核心挑战:如何让大语言模型(LLM)准确掌握企业内部知识并避免产生幻觉(Hallucination)?检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation,RAG)技术应运而生,它通过将信息检索与生成模型相结合,有效解决了这一难题。
Spring AI作为Spring官方推出的AI开发框架,为Java开发者提供了构建AI应用的标准化方案。结合Redis这一高性能向量数据库,我们可以构建出响应迅速、成本可控、易于维护的RAG问答系统。本文将深入探讨这一技术组合的架构设计、核心实现和优化策略。
一、RAG技术架构设计
1.1 系统整体架构
基于Spring AI和Redis的RAG系统主要包含以下组件:
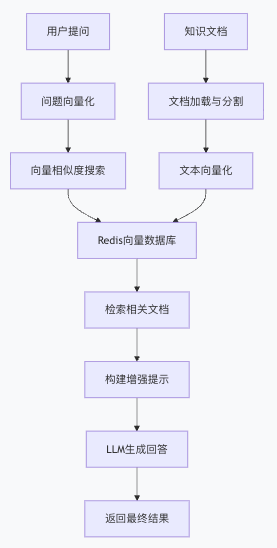 图片
图片
1.2 技术栈选型依据
- Spring AI:提供统一的AI应用开发接口,支持多种大模型和向量数据库
- Redis Stack:具备向量搜索能力的高性能内存数据库,适合实时检索场景
- OpenAI API/本地模型:平衡性能与成本的需求
二、环境准备与核心配置
2.1 项目依赖配置
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Redis 向量存储 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-vector-store-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-redis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-pdf-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 文档解析(支持 Word、Excel 等) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-tika-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
2.2 应用配置文件
# application.yml
spring:
ai:
openai:
embedding:
options:
model: text-embedding-v4 # 使用百炼平台的嵌入模型
vectorstore:
redis:
uri: redis://localhost:6379
index: knowledge-base
prefix: "doc:"
initialize-schema: true
server:
port: 8080- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
三、核心实现源码解析
3.1 数据加载服务实现
知识库的初始化是RAG系统的基础,需要将文档转换为向量并存储到Redis中。
@Service
@Slf4j
public class DataLoaderService {
@Value("classpath:knowledge/*.pdf")
private Resource[] knowledgeResources;
@Autowired
private VectorStore vectorStore;
@PostConstruct
public void initializeKnowledgeBase() {
log.info("开始初始化知识库...");
for (Resource resource : knowledgeResources) {
try {
// 使用PDF文档阅读器
PagePdfDocumentReader pdfReader = new PagePdfDocumentReader(
resource,
PdfDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.withPagesPerDocument(1)
.build()
);
// 文本分割器,确保文档块大小合适
TokenTextSplitter textSplitter = new TokenTextSplitter(
1000, // 最大token数
200, // 重叠token数
true // 分段存储
);
// 读取、分割并存储文档
List<Document> documents = pdfReader.get();
List<Document> chunks = textSplitter.apply(documents);
vectorStore.add(chunks);
log.info("已加载文档: {},分割为 {} 个块",
resource.getFilename(), chunks.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("加载文档失败: {}", resource.getFilename(), e);
}
}
log.info("知识库初始化完成");
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
3.2 RAG服务核心逻辑
RAG服务的核心在于实现检索与生成的协同工作。
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RagService {
@Autowired
private VectorStore vectorStore;
@Autowired
private ChatClient chatClient;
// 相似度搜索配置
private static final int TOP_K = 5;
private static final double SIMILARITY_THRESHOLD = 0.7;
public Generation retrieve(String userQuery) {
// 1. 向量相似度搜索
SearchRequest searchRequest = SearchRequest.query(userQuery)
.withTopK(TOP_K)
.withSimilarityThreshold(SIMILARITY_THRESHOLD);
List<Document> relevantDocs = vectorStore.similaritySearch(searchRequest);
if (relevantDocs.isEmpty()) {
return new Generation("未找到相关信息,请尝试其他问题。");
}
// 2. 构建增强提示
String context = buildContext(relevantDocs);
String enhancedPrompt = buildEnhancedPrompt(userQuery, context);
// 3. 调用LLM生成回答
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(enhancedPrompt);
ChatResponse response = chatClient.call(prompt);
return response.getResult();
}
private String buildContext(List<Document> documents) {
StringBuilder contextBuilder = new StringBuilder();
contextBuilder.append("相关参考信息:\n\n");
for (int i = 0; i < documents.size(); i++) {
Document doc = documents.get(i);
contextBuilder.append(String.format("[%d] %s\n\n", i + 1, doc.getText()));
}
return contextBuilder.toString();
}
private String buildEnhancedPrompt(String userQuery, String context) {
return String.format("""
你是一个专业的客服助手,请根据以下参考信息回答问题。
如果参考信息不足以回答问题,请明确说明。
不要编造信息,保持回答准确、简洁。
%s
用户问题:%s
请根据以上信息提供回答:
""", context, userQuery);
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
3.3 控制器层实现
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/rag")
@Slf4j
public class RagController {
@Autowired
private RagService ragService;
@PostMapping("/chat")
public ResponseEntity<ChatResponse> chat(@RequestBody ChatRequest request) {
try {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Generation generation = ragService.retrieve(request.getQuestion());
long responseTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
log.info("问题处理完成: 问题长度={}, 响应时间={}ms",
request.getQuestion().length(), responseTime);
ChatResponse response = new ChatResponse(
generation.getOutput().getContent(),
responseTime
);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("处理问题时发生错误", e);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(new ChatResponse("系统繁忙,请稍后重试", -1));
}
}
// DTO类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class ChatRequest {
private String question;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class ChatResponse {
private String answer;
private long responseTimeMs;
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
四、高级特性与优化策略
4.1 使用QuestionAnswerAdvisor优化RAG流程
Spring AI提供了Advisor接口来标准化RAG流程的实现。
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class RagAdvisorConfig {
@Bean
public QuestionAnswerAdvisor questionAnswerAdvisor(
VectorStore vectorStore,
ChatClient chatClient) {
return new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(vectorStore, chatClient) {
@Override
public Prompt before(String question) {
// 自定义检索逻辑
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.query(question)
.withTopK(5)
.withSimilarityThreshold(0.75)
.withFilterExpression("category == 'technical'");
List<Document> docs = vectorStore.similaritySearch(request);
// 构建系统消息
SystemMessage systemMessage = new SystemMessage(
"你是一个技术专家,请根据以下文档回答问题:\n" +
docs.stream()
.map(Document::getText)
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n\n"))
);
UserMessage userMessage = new UserMessage(question);
return new Prompt(List.of(systemMessage, userMessage));
}
@Override
public String after(ChatResponse response) {
// 后处理:添加引用和验证
String answer = response.getResult().getOutput().getContent();
return answer + "\n\n*以上信息仅供参考*";
}
};
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
4.2 性能优化实践
向量索引优化
spring:
ai:
vectorstore:
redis:
index-type: HNSW # 使用分层导航小世界算法
distance-metric: COSINE # 余弦相似度
index-options: |
{
"EF_CONSTRUCTION": 200,
"M": 16
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
缓存策略实现
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CachingRagService {
@Autowired
private RagService ragService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
private static final long CACHE_TTL = 3600; // 1小时
public Generation retrieveWithCache(String userQuery) {
// 生成查询指纹作为缓存键
String cacheKey = generateCacheKey(userQuery);
// 尝试从缓存获取
String cachedAnswer = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (cachedAnswer != null) {
log.debug("缓存命中: {}", cacheKey);
return new Generation(cachedAnswer);
}
// 缓存未命中,执行RAG流程
Generation generation = ragService.retrieve(userQuery);
// 缓存结果
if (shouldCache(generation)) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
cacheKey,
generation.getOutput().getContent(),
Duration.ofSeconds(CACHE_TTL)
);
}
return generation;
}
private String generateCacheKey(String query) {
return "rag:cache:" + Integer.toHexString(query.hashCode());
}
private boolean shouldCache(Generation generation) {
// 只缓存高质量的回答
String content = generation.getOutput().getContent();
return !content.contains("不确定") && !content.contains("无法回答");
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
五、实战案例:企业知识库问答系统
5.1 系统特色功能
基于Spring AI和Redis的RAG系统在实际应用中表现出色:
- 精准问答:针对”公司请假流程是什么?”等问题,能直接从员工手册中检索相关信息生成准确回答
- 多文档支持:支持PDF、Word、HTML等多种格式文档的自动处理和向量化
- 实时更新:知识库更新后,系统能够立即感知并提供最新信息
5.2 性能对比数据

六、总结与展望
Spring AI与Redis的结合为Java开发者提供了构建高性能RAG系统的理想方案。通过本文介绍的架构设计和实现方案,企业可以快速搭建属于自己的智能问答系统,显著提升知识管理效率。
未来,随着Spring AI生态的不断完善,我们可以期待更多高级特性的出现:
- 多模态RAG:支持图像、表格等非文本内容的检索与生成
- 自适应学习:系统能够根据用户反馈自动优化检索策略
- 边缘部署:支持在资源受限环境中运行轻量级RAG系统
文章来自:51CTO
